Science & Tech
Ellie Abraham
Apr 01, 2025
Mars May Once Been Host to Beautiful Sandy Beaches Next to Vast …
ZMG - Amaze Lab / VideoElephant
NASA’s Perseverance rover has stunned experts after finding some strange-looking rock composed of spherules on the surface of Mars.
The team studying the Perseverance rover’s discoveries were astonished by the formation, which was snapped by cameras onboard the rover earlier this month, which landed on the Red Planet in February 2021.
The rock is made up of hundreds of millimetre-sized spheres and has left scientists puzzled by their origin.
The image of the rock was captured when the Perseverance rover was at Broom Point, at the lower slopes of the Witch Hazel Hill on the rim of the Jezero crater, where a series of light and dark-toned bands had been seen.
“Orbital views of Witch Hazel show layered materials that likely date from a time when Mars had a very different climate than today,” NASA explained, ahead of the mission.
There, the rover was able to sample some of the rock, which is where the bizarre rock texture was discovered. Named “St. Pauls Bay” by the team, the rock was found to be made up of hundreds of dark grey spheres.
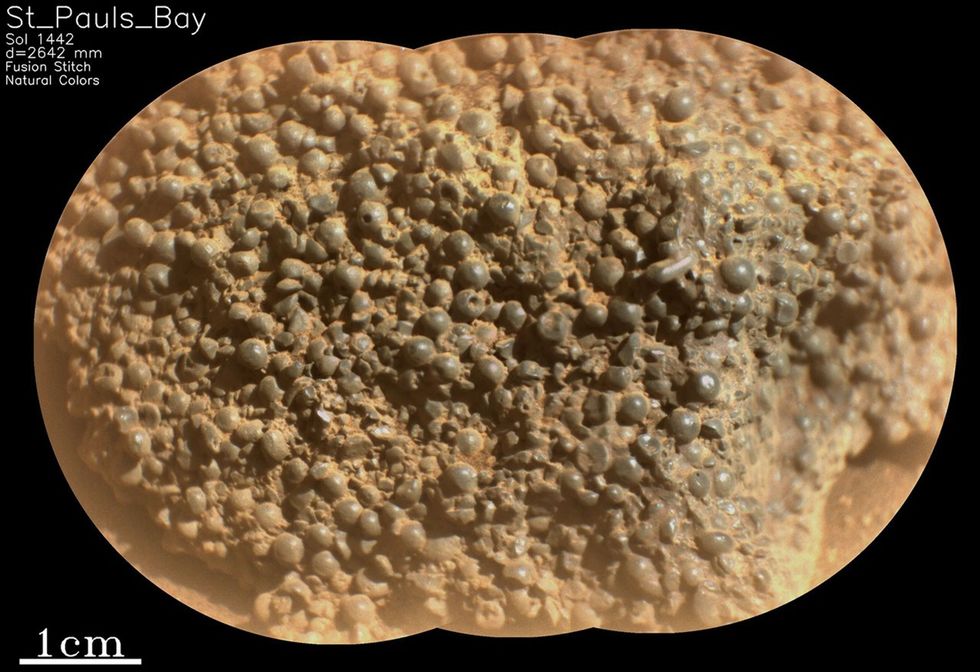
“Some of these occurred as more elongate, elliptical shapes, while others possessed angular edges, perhaps representing broken spherule fragments. Some spheres even possessed tiny pinholes!” NASA explained in an update.
And it’s not the first time these kinds of spheres have been found, as slightly larger, so-called “Martian Blueberries”, were discovered on Mars in 2004 at Meridiani Planum. Meanwhile, in 2013, the Curiosity rover observed spherules in the rocks of Yellowknife Bay at Gale crater.
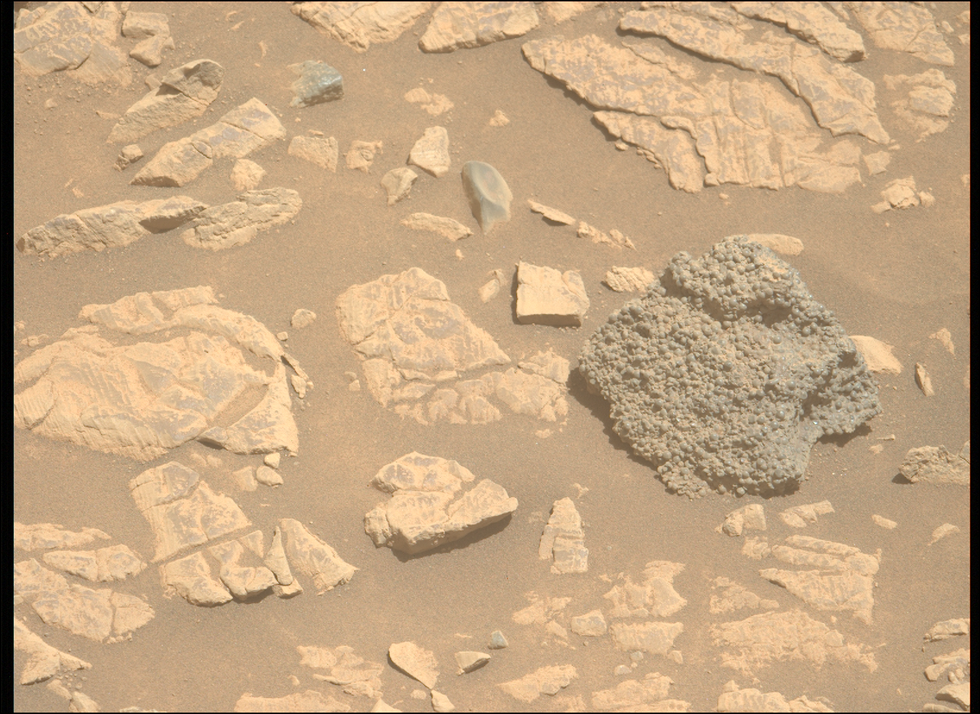

NASA said: “In each of these cases, the spherules were interpreted as concretions, features that formed by interaction with groundwater circulating through pore spaces in the rock. Not all spherules form this way, however.
“They also form on Earth by rapid cooling of molten rock droplets formed in a volcanic eruption, for instance, or by the condensation of rock vaporized by a meteorite impact.”
The team are now working to determine how and why the spheres of the St. Pauls Bay rock specifically were formed.
This article was originally published on 27 March 2025
Why not read…
“Stranded” NASA astronauts will not receive overtime pay
NASA Mars rover makes discovery “unlike anything we’ve seen before”
Dusty and cold Mars once had sandy beaches - what happened?
Sign up for our free indy100 weekly newsletter
How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel
Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings
Top 100
The Conversation (0)














