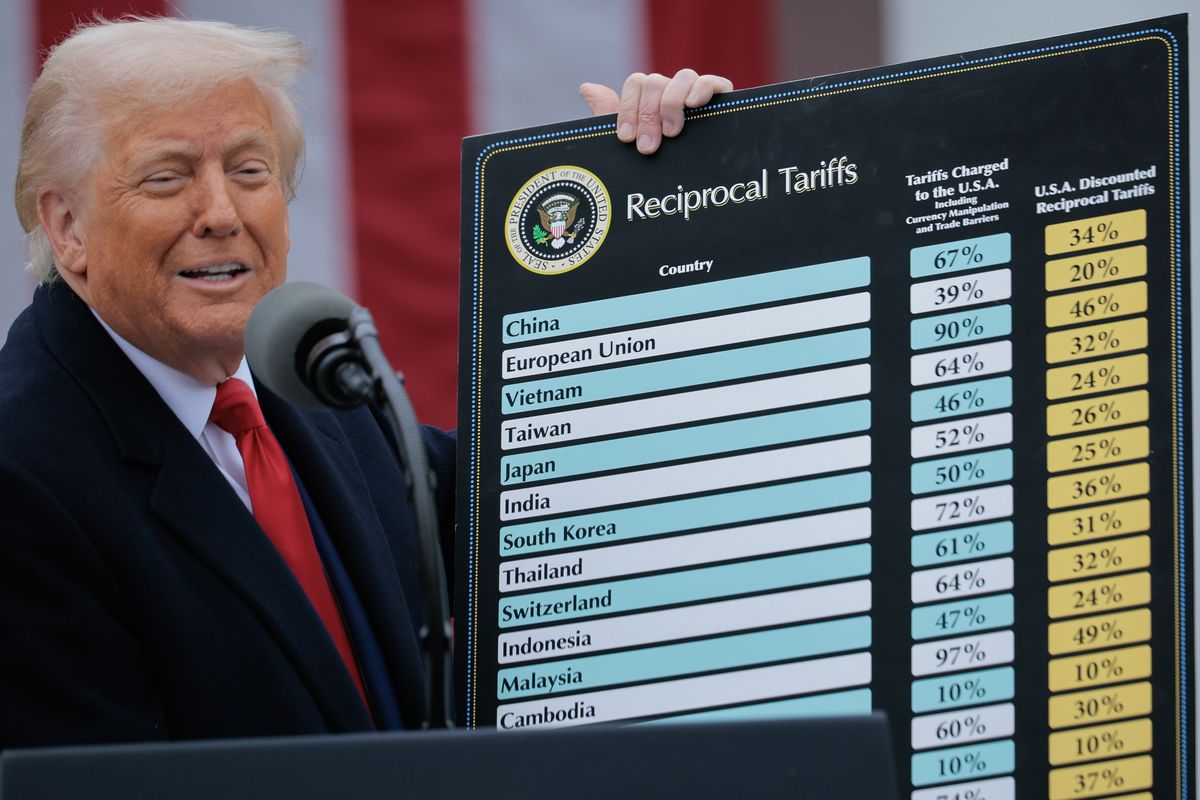
Science & Tech
Catherine Shuttleworth
Oct 07, 2023
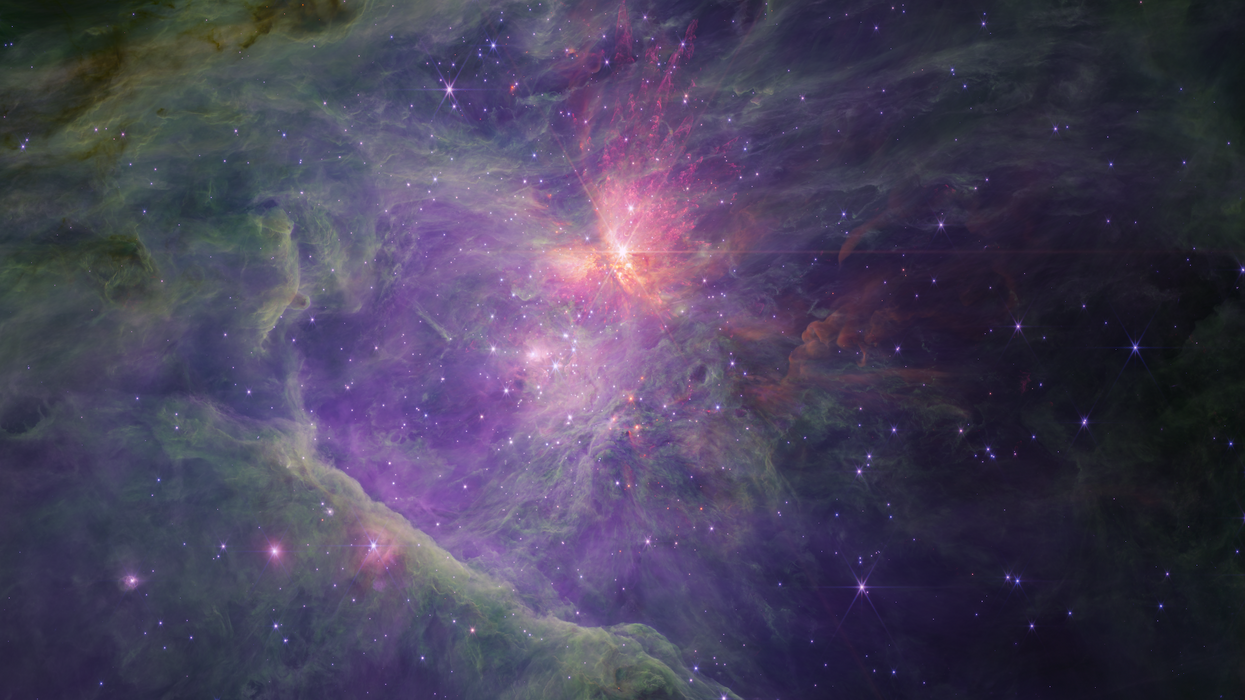

New discovery of rogue planets defies scientific theory and leaves experts baffled
NASA, ESA, CSA
Planet-like objects in the Orion Nebula have been revealed for the first time in images from the James Webb Space Telescope.
The Orion Nebula, one of the brightest nebulae in the night sky, has long presented astronomers with an abundance of celestial objects to study. It is identifiable as the sword in the Orion constellation and is located 1,300 light-years from Earth.
Astronomers managed to discover unprecedented details by capturing mosaics of the Orion Nebula in short and long wavelengths of light.
Whilst searching for low-mass objects, astronomers Samuel G. Pearson - a European Space Agency research fellow at the European Space Research and Technology Centre in the Netherlands - and Mark J. McCaughrean - senior adviser for science and exploration at the European Space Agency - came across something they had never before seen. Their discovery appears to defy some fundamental astronomical theories: pairs of planet-like objects with masses between 0.6 and 13 times the mass of Jupiter.
They have been dubbed Jupiter Mass Binary Objects, or JuMBOs.
"Although some of them are more massive than the planet Jupiter, they will be roughly the same size and only slightly large," said Pearson.
The astronomers found 40 pairs of JuMBOs, and although they exist in pairs, the objects are typically about 200 astronomical units apart, or 200 times the distance between Earth and the sun. This means it can take between 20,000 and 80,000 years for the objects to complete an orbit around each other.
McCaughrean and Pearson have written two research papers based on their discoveries in the Orion Nebula. The preliminary findings are available on a preprint site called arXiv whilst the studies have been submitted to academic journals for publication. But many questions about JuMBOs remain.
"Scientists have been working on theories and models of star and planet formation for decades, but none of them have ever predicted that we would find pairs of super low mass objects floating alone in space - and we're seeing lots of them," Pearson said. "The main that we learn for this is that there is something fundamentally wrong with either our understanding of planet formation, star formation, or both."
Sign upto our free Indy100 weekly newsletter
Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
Top 100
The Conversation (0)