News
Steve Connor
Aug 11, 2015
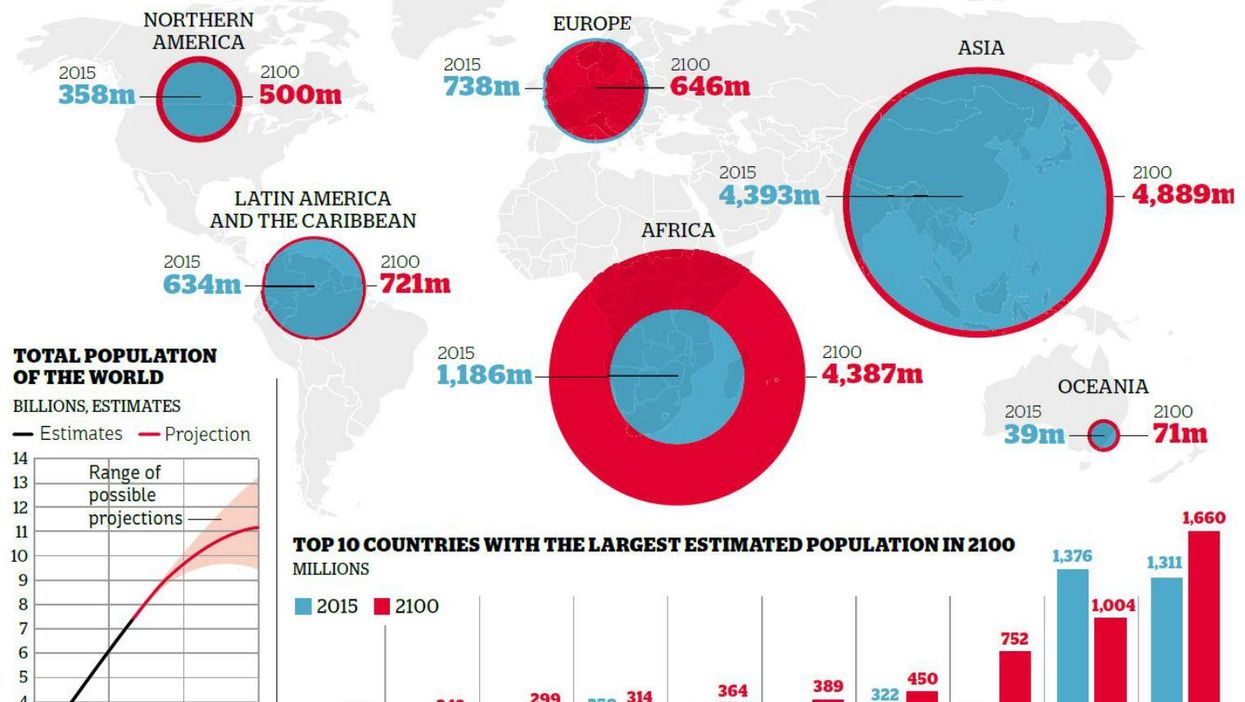
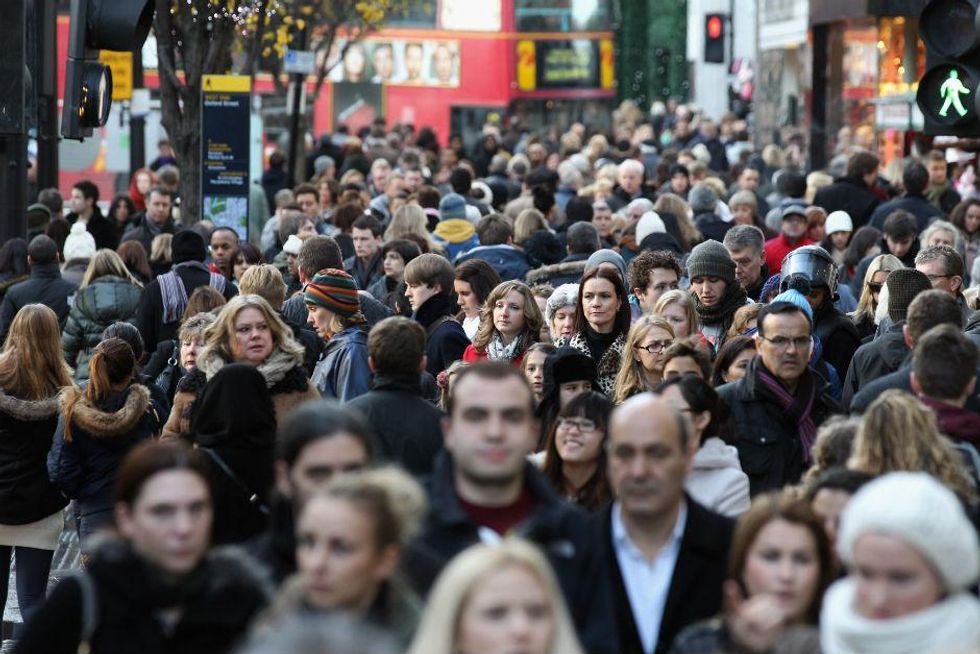
Africa will account for much of the explosive growth in the world’s population this century, which is expected to rise from 7.3 billion today to 11.2 billion by 2100, according to the latest UN forecasts.
Fertility rates – the average number of children born per woman – have declined globally but they are not decreasing as fast in Africa as on other continents, said John Wilmoth, director of the UN Population Division in New York.
In countries such as Nigeria, Africa’s most populous nation, there are now signs that fertility rates are again on the rise, which could have a significant impact on future estimates of global population, Mr Wilmoth said.
These will be the 10 most populous nations on Earth in 2100, according to the latest projections:
1. India 1.66bn
2. China 1.004bn
3. Nigeria 752m
4. US 450m
5. DR Congo 389m
6. Pakistan 364m
7. Indonesia 314m
8. Tanzania 299m
9. Ethiopia 243m
10. Niger 209m
The concentration of population growth in the poorest countries will make it harder for those governments to eradicate poverty and inequality, combat hunger and malnutrition, expand education enrolment and health systems, improve the provisions of basic services and implement other elements of a sustainable development agenda to ensure that no-one is left behind.
- UN
The population boom will likely put significant stress on governments’ ability to eradicate hunger and malnutrition, according to the UN.
According to the latest UN projections, there is unlikely to be an end to the growth of the global human population this century unless there are unprecedented declines in fertility rates in those parts of sub-Saharan Africa still experiencing rapid growth – the UN estimates that there is less than a 1 in 4 chance of an end to global population growth by 2100.
More: These will be Europe's most-populated countries by 2050
Top 100
The Conversation (0)














